How to Choose the Right Halyard/Sheet
When choosing a halyard for your sailboat, several factors come into play. These include the weight of the sail, the type of sail, the sailboat’s size, and the expected wind conditions. You should also consider the halyard’s stretch, which affects sail shape and performance. It is essential to choose a halyard that matches the load the sail will have on the line. Low-stretch halyards are ideal for racing and performance sailing, where every fraction of a knot counts.
Some Things to Consider when Choosing a Halyard or Sheet Include:
- Material: The material you choose for your line can affect its strength, durability, and stretch resistance.
- Diameter: The diameter of your halyard or sheet should be appropriate for the load the sail will apply to it and the size of your boat.
- Length: The length of your halyard or sheet should allow you to run your lines wherever they are needed, plus some extra for you to trim and tie off with.
- Attachment: The type of attachment you choose for your halyard or sheet can change depending on how you run your sheets and how the head of your sail is configured.
- Review Your Options: Making a decision about lines can be daunting, luckily Precision Sails has made it easy for you to pick your halyard or sheets by simplifying the process into two groups and pre-selecting the diameter, length, and attachment for your boat and line.
Here is a Quick Guide to Explain Material Choice:
The Precision Cruising series employs high-quality polyester lines, which are a good all-around option for starting and performing well. Polyester halyards and sheets are the most common and suitable for most sizes of sailboats, but they do stretch more than other lines like dyneema, spectra, or stirotex, which can affect sail shape and performance.
To address this, the Precision Performance series focuses on using stronger and stretch-resistant inner cores, making them ideal for racing sailboats that require high precision and tight tolerances. These lines are made of stirotex, which you may recognize by the name of spectra or dyneema. Stirotex is a chemically identical variation. The parent compound in these high-tension lines is HMPE. These lines are the strongest and least stretchy, making them the top choice for high-performance racing sailboats.
How to Maintain Your Halyards, Sheets, and Lines
Proper maintenance of your halyards is crucial for their longevity and reliability. Some tips for maintaining your halyards include:
Maintenance Checklist
- Regular inspection: Check your lines regularly for signs of wear, fraying, or damage.
- Cleaning: Clean your halyards and sheets periodically with soap and water to remove dirt and salt buildup.
- Lubrication: Lubricate your halyards and sheets with a silicone spray or dry lubricant to reduce friction and wear.
- Storage: When not in use, store your lines coiled neatly and out of direct sunlight if you can.
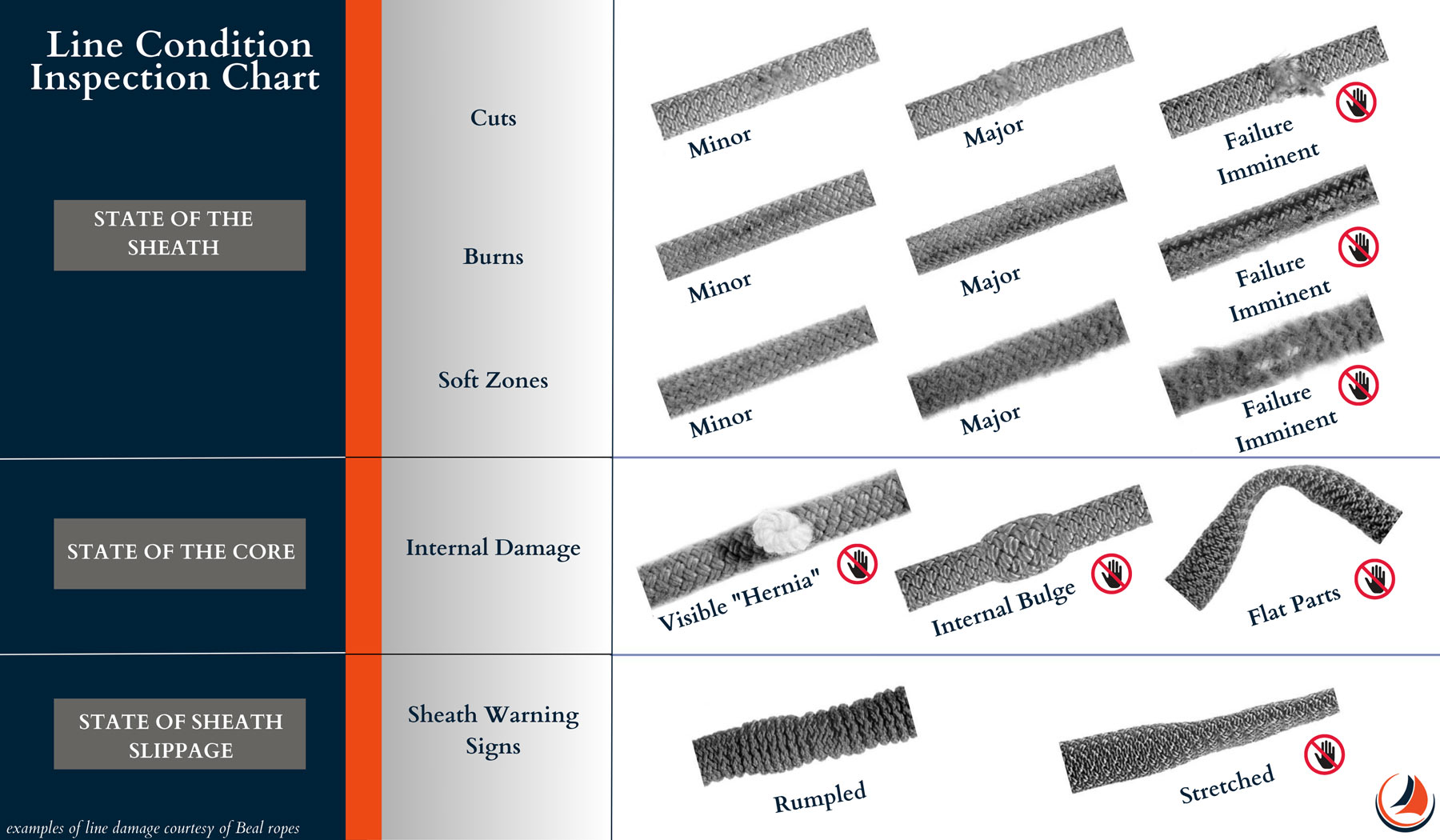
Signs of Wear – How to Inspect Your Lines
Lines that show obvious signs of deterioration must be discarded and replaced immediately. One of the most apparent and hazardous signs of wear on a line is a cut or damaged sheath that exposes the core. In such cases, it is important to retire the line immediately to prevent any further damage or potential failures.
Other signs may include hardness around the sheath or fuzziness. These signs may be particularly evident near the connection points or any areas of high friction. It’s also important to pay attention to any changes in the handling or feel of the line, as this may indicate internal damage or other issues that require attention.
A way to protect your investment is proper care and cleaning and avoiding the use of harsh chemicals or high-pressure washers, which can damage the fibers. This can be done by soaking them in a bucket of warm water with mild soap or detergent, then rinsing thoroughly and allowing them to air dry. This helps to remove any salt, dirt, or grime that may have accumulated, which can cause premature wear and tear if left unchecked.
A way to visualize this is to envision dirt particles getting trapped between the fibers of the line and causing small tears in the weave. When the line is put under tension, these dirt particles act like miniature saw blades, gradually weakening the line over time and potentially leading to catastrophic failures. Therefore, regular cleaning and maintenance of your lines, including halyards and sheets, is essential to ensure their longevity and reliability and to avoid any dangerous situations while out on the water.
Inspecting Your Lines for Damage
Pro tip: Usage level and proper care is a more important indicator than age
Let’s dispel some common misconceptions about when to retire a sailboat line. For example, some sailors may retire a line based solely on its age, rather than its condition. We want to stress the importance of inspecting lines regularly and retiring them when signs of wear or damage are detected, regardless of their age. Here’s a helpful checklist so you know what to look for on your lines.
Inspection Checklist
- Check for visual signs of wear and tear, such as fraying or abrasions, which can weaken the line and compromise its strength. Be sure to examine the line thoroughly, paying particular attention to any areas of high friction or wear.
- Run your hands along the length of the line, feeling for any hard or soft spots, which can indicate internal damage or wear. If you detect any abnormalities, consider retiring the line or seeking professional advice.
- Look for any signs of UV damage, which can cause the line to degrade over time. This is particularly important for lines that are exposed to sunlight for extended periods.
- Check the diameter of the line, ensuring that it matches the manufacturer’s specifications. Any significant deviations may indicate that the line has been stretched or otherwise damaged.
- Examine the connection points, including splices and knots, ensuring that they are secure and free from any signs of wear or damage.

Overview
To recap, lines, halyards, and sheets are an essential component of any sailing vessel, and choosing the right halyard for your boat is a necessary part of outfitting your vessel. Regular maintenance and proper care of your halyards can ensure their longevity and reliability. We hope this article has provided valuable insights into halyards, sheets, and lines, though we understand that it may seem like a lot of information.
If you feel overwhelmed by the amount of information, don’t worry, we have simplified the process of finding the right line for your boat. Simply fill out a form, and we will send you the best fit and our professional opinion based on the type of sailing you plan on doing. If you have any questions, comments, or wish to order lines from our sail consultants, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQ’s
Q: What is a sailboat halyard?
A: Halyards are ropes or lines used to hoist sails, flags, and other equipment on a boat.
Q: What is a sailboat sheet?
A: A sailboat sheet is a line that is attached to the lower corner of a sail and used to control its position relative to the wind. The sheet is usually led through a block or a series of blocks, which allow the sailor to adjust the sail’s angle and trim it for maximum efficiency. In addition to controlling the sail’s position, the sheet also helps to control the sail’s shape and tension, which can affect the boat’s speed and handling.
Q: Can different types of materials be used to make halyards, sheets, and lines?
A: Yes, lines can be made of various materials such as polyester, nylon, stirotex, and dyneema. Each material has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of material depends on the type of sailing and personal preference.
Q: How do I determine the length of halyard I need for my sailboat?
A: It’s important to consult with a sail consultant or experienced sailor to ensure you get the correct length. The length of halyard you need will depend on the height of your mast, the type and size of the sail you will be using, and where you plan on trimming your sails. Calculating the length is more complex than simply taking a guess, not to worry though, we have made it easy. Give us a call or fill out our form to let our system crunch the numbers for you.
Q: How do I know if my halyard or sheets are due for replacement?
A: Look for signs of wear and tear such as fraying, kinking, or stretching. If the line feels stiff or brittle, it may be time to replace it. Additionally, if you notice any damage to the sheave or winch, this may also indicate the need for a replacement. See the checklist above for detailed instructions.
Q: Are there any safety precautions I should take when using halyards and sheets?
A: Yes, it’s important to properly understand how to use a winch and don’t wrap the rope around your arm or fingers. Always be aware of your surroundings and avoid getting entangled in halyards or other lines. It’s also recommended to have a backup halyard in case of failure or emergency situations.
Q: How can halyards affect the performance of a sailboat?
A: The type of halyard used can have an impact on the performance of the sailboat. For instance, a stretchy halyard may cause the sail to lose its shape by releasing the tension on the sail over time, while a stretch-resistant halyard can help the sail maintain its shape in strong winds.
Q: Is it possible to splice or repair a damaged halyard or sheet?
A: It is possible to splice or repair a damaged halyard, depending on the extent of the damage and the material of the halyard. However, it’s essential to have the repair done by a professional or experienced sailor to ensure the halyard’s continued reliability and safety.
Q: How often should I replace my lines?
A: The lifespan of halyards and sheets can vary depending on factors such as usage, exposure to weather, and material. It’s recommended to regularly inspect your lines for wear and tear and replace them as needed. Condition is a much stronger indicator than age. Assuming light use and good condition, some materials like Stirotex have a longer lifespan, other materials may need to be replaced more often. In general, halyards and sheets should be replaced every 3-5 years for optimal safety and efficiency.